New Evidence Challenges Everything We Know About the Universe

In the ever-expanding and boundless realm of cosmology, where knowledge sees no limits, another piece of evidence supporting a mind-boggling theory has been uncovered recently by Computer Scientist Lior Shamir. Whilst the theory of our universe existing inside a black hole has been proposed for a while, efforts trying to prove it were met with failure. But this recent paper has been making rounds in academia due to its unexpected results.
The paper uses the spectacular James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to analyse 263 galaxies whose data was collected as part of the James Webb Space Telescope Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey, or "JADES." The analysis demonstrates that two thirds of these galaxies have a clockwise spin while the rest show a counter clockwise direction. This is truly perplexing; because the laws of physics should act the same in every portion of the universe, that is, the universe doesn’t have any special places or directions, so we would expect it to have no net galactic rotation. This translates to a roughly even number of galaxies spinning in opposite directions, but the data says otherwise!
This can only be explained in two ways, Shamir says, one being the aforementioned black hole cosmology which hints at our universe being born while rotating, that is, inside of a black hole. Theoretically, what would that even look like?
As mentioned before, a number of physicists currently champion the theory of our universe originating from the gravitational collapse of a supermassive, hyper-dense mass of fermionic matter. Another paper like this tries to set up a new mathematical model for the birth of our universe.
We all have, at some point, heard the word ‘singularity’ in discussions regarding black holes; the singularity is a point where matter is considered to be infinitely dense and spacetime infinitely curved due to the collapse of elephantine amounts of matter to one single point. In modern physics, however, it is entirely theoretical like any other infinities. On the contrary, physicists believe that their current theories are insufficient, and that there are other effects related to quantum gravity which prevent the existence of infinite density. The model proposes the following sequence of events: following the collapse of a supermassive galactic mass, the system reaches an ultra-dense state, which then undergoes a bounce, rebounding outward into a phase of rapid expansion.
This is facilitated by something known as the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that No two fermions (particles like electrons, protons etc.) can be in the exact same place doing the exact same thing at the same time, that is, have identical quantum states in the same system. This principle is why electrons occupy different shells on atoms. Consequently, these fermions prevent a singularity from forming and lead to the Big Bounce: the rebound caused by the pressure generated due to the Pauli Exclusion Principle. The expansion that follows mathematically resembles the Big Bang!
Scientists suggest that if this theory holds true, the axis of rotation of the parent black hole could imprint itself onto the universe within it as a preferred cosmic spin direction, which Shamir may have detected.
However, we should not jump to conclusions. For starters, the sample size is diminutive compared to the billions of galaxies that exist in the universe. Moreover, there remains another, albeit exponentially less thrilling, possibility: that the apparent imbalance in galaxy rotations is influenced by the rotation of our own Milky Way. Shamir intends to recalibrate distance measurements for more distant galaxies in order to minimize the influence of our own galaxy’s rotation on observational data. Until then, physicists are left only to wonder if this is substantial evidence of a deeper, unexplored truth or just another one of the tricks the universe has up front to confuse humans.
Similar Post You May Like
-
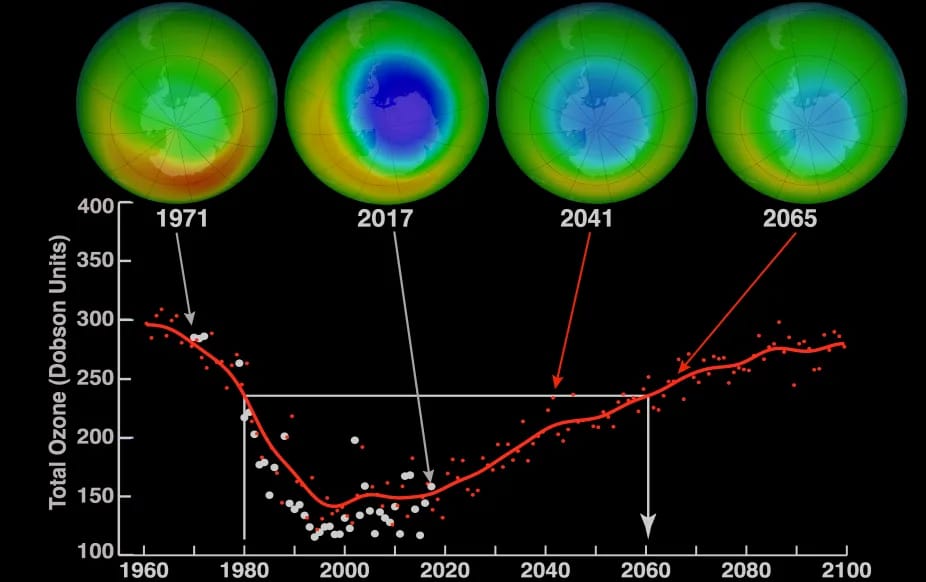
CFCs, HFCs and their long, troubled history
At its peak, the ozone hole covered an area 7 times larger than the size of Europe, around 29.9 million km2, and was rapidly expanding
-

The Origin of Universe: Deciding point where it all began!
Let us unravel and surf through the ideas throughout ages to understand what the universe and its origin itself was to its inhabitants across history.
-

The Artemis Program
Inspired by the Greek goddess of the Moon, twin sister to Apollo, the artimis program was named on 14 May 2019 by Jim Bridenstine.






