Why Sundays Are Prohibited For The Sun Itself?
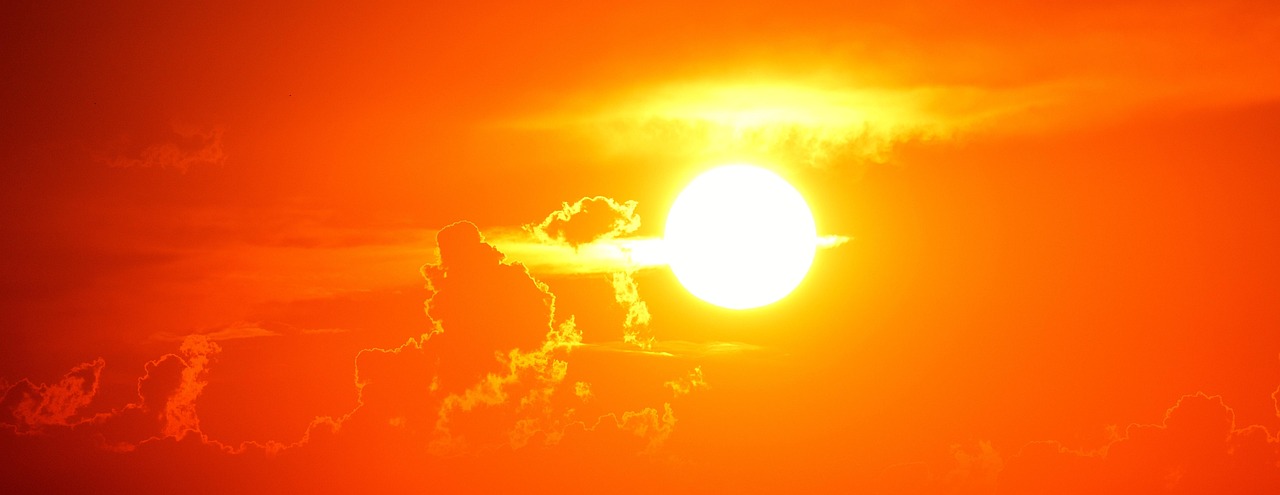

According to heliophysics, apart from the eight planets forming the solar system, it is astonishing that the centrally located Sun is the only star within it. Estimated to be nearly 4.5 billion years old, the Sun is a massive ball that omits hydrogen and helium in plasma form. It is the only star where gases are ionized and particles have altered electron counts.
The hydrogen, which makes up about 75% of the Sun, is constantly merging through nuclear fusion, producing helium and unleashing enormous energy (heat and light) essential to thriving life on Earth. The Sun is approximately 150 million kilometers away from the Earth, which supports the calculation for the light to travel from the Sun to the Earth—8 and a half minutes to be exact.
As small as it's visible from the Earth, it's actually a giant star which is 100 times greater than the size of Earth, making itself enough to be the only star needed to hold the entire solar system in its orbit due to its overly strong gravitational pull. The Sun is a source of radiation resulting from nuclear reactions, with temperatures varying significantly from its core to its surface. The core reaches an extreme 15 million °C, while the surface maintains a comparatively cooler 5,500°C.
The difference in the temperature goes even beyond a sounding mystery where the surrounding of the surface of the Sun, the “corona,” is actually hotter than the Sun’s surface itself (2 million °C). With this logic, as far as the corona stretches, the temperature rises, making life on the Sun impossible.
The extremely important energy required from the Sun is evidenced since the Sun was energized when it was struck by a shockwave emitted by a nearby supernova. While studying the Sun in regards to making life on Earth feasible, it is significant to observe the speed the Sun’s energy travels from Sun to Earth, which is traveling at the speed of light in the form of electromagnetic radiation as waves of various wavelengths and frequencies, out of which the most known and harmful one is the ultraviolet radiation, which is entirely absorbed in the Earth’s atmosphere. And for the heat, the Sun also emits infrared radiations.
Scientific history has long acknowledged the traits of this star, highlighting to the scientists its unique characteristics, each of which is vital for sustaining life on Earth. The Sun’s abundant radiation is the driving force behind solar energy technology, which utilizes its power to provide us with heat, light, and electricity. As a renewable energy source, solar power is a game-changer, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels and reducing our reliance on non-renewable resources.
Innovative technologies like photovoltaic systems, solar water heaters, concentrated solar power, and building-integrated solar design are making it possible to tap into the Sun’s energy, reducing our carbon footprint and promoting a cleaner, greener future.
In addition, when it comes to fossil fuels, the process progresses through ancient photosynthesis, where aquatic plants that emerged around three billion years ago used the Sun’s sunlight to grow and thrive. But as these plants died and sank deeper into the earth, they were transformed into fossil fuels over millions of years. The Sun’s energy, captured through photosynthesis, was effectively stored in these ancient microorganisms, which eventually became the petroleum, natural gas, and coal that power our world.
This highlights the Sun’s significant contribution to our energy resources, emphasizing the importance of exploring renewable energy sources. The Sun’s energy is the driving force behind the food web, thanks to photosynthesis. Plants and algae, the primary producers, use sunlight to convert it into energy. As the base of the food web, these producers support the entire ecosystem, passing on their energy and nutrients to every other living being.
All these functions of the Sun might seem few, but is life on Earth ready to survive without this giant star? What if the Sun decides to sign off for a Sunday for itself?
Although this scenario seems nearly impossible, let us imagine Earth without the Sun: for the initial 8 and a half minutes, the Earth would still be oblivious to this experience, and finally, after the 9th minute, it would be left with darkness. The Sun being the source to reflect lights on celestial bodies—thus, without these celestial bodies, including the moon—it would no longer be visible, and the sudden cease of emitting heat would drastically drop the Earth’s temperature.
Luckily, Earth does have a natural ability to retain heat, so there won’t be an immediate freeze. However, the effects would still be severe, and life on Earth would become extremely challenging right away. A factor to add here is that this drop in temperature won’t stop. In just one year, the average temperature on Earth could go below -37.77 °C. That’s even colder than Antarctica in the winter.
By then, the surface of the oceans would be completely frozen, which would have a devastating impact on our planet’s ecosystem, although the deep layers of water would stay liquid for a very long time. Eventually, though, everything will freeze—even the air, the whole atmosphere. If anyone was still alive, they would be exposed to harsh radiation from space, destroying every surviving life form.
Lastly, the sudden disappearance of the Sun would be a complete full stop to life, as photosynthesis would come to a halt, and all plants would eventually die off. This will have a ripple effect throughout the entire food chain. Since humans and animals rely on plants for food, there is the potential for possible extinction. While some people might be able to survive for a short period using stored food and resources, ultimately, life on Earth would be unsustainable without the Sun’s energy.
Conclusion
As sad as it sounds, the Sun could never have a Sunday or take a day off, as it serves as the foundation of life on Earth. Its sudden disappearance would lead to catastrophic consequences, including plunging the planet into darkness and rendering life unsustainable. The food chain would collapse, oceans would freeze, and the atmosphere would vanish. Humans and animals would struggle to survive, and eventually, all life on Earth would cease to exist. The Sun’s energy is not just a luxury but a necessity for the survival of life on Earth.
Similar Post You May Like
-
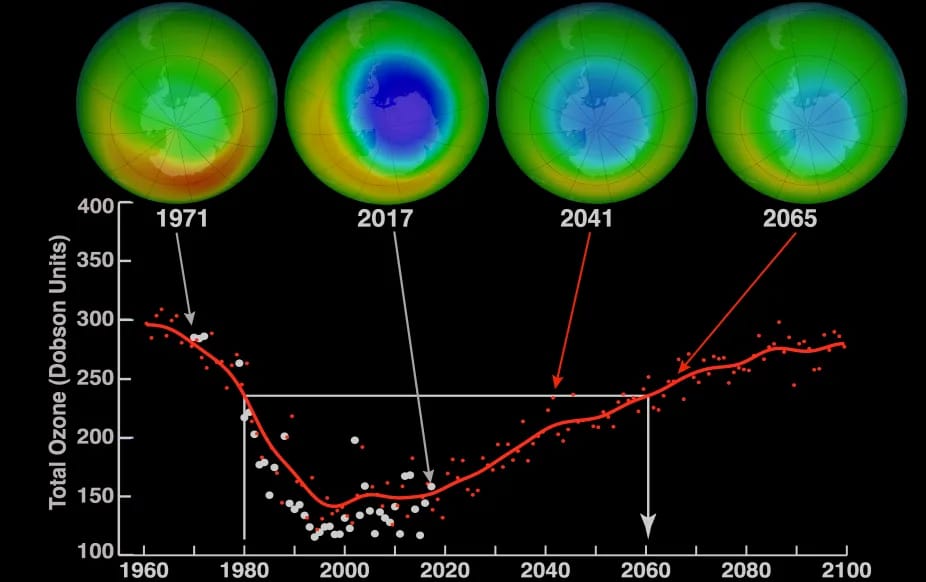
CFCs, HFCs and their long, troubled history
At its peak, the ozone hole covered an area 7 times larger than the size of Europe, around 29.9 million km2, and was rapidly expanding
-

The Origin of Universe: Deciding point where it all began!
Let us unravel and surf through the ideas throughout ages to understand what the universe and its origin itself was to its inhabitants across history.
-

The Artemis Program
Inspired by the Greek goddess of the Moon, twin sister to Apollo, the artimis program was named on 14 May 2019 by Jim Bridenstine.






